- Understanding Azure Container Apps Architecture
- Environments: Secure Boundaries for Container Apps
- Revision Management: Seamless Application Updates
- Automatic Scaling: Handling Dynamic Workloads
- Service Discovery: Simplifying Microservices Communication
- Docker Integration and Containerization
- Flexible Container Registry Options
- Real-World Example: Migrating a Monolithic Application
- Monitoring and Observability
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
When organizations seek agility and scalability, they turn to containerization—the driving force behind modern application deployment. Azure Container Apps, Microsoft's innovative serverless container service, paired with the power of Docker, empowers organizations to build applications that thrive under dynamic workloads. In this blog, we’ll uncover how Azure Container Apps redefines enterprise deployment, offering a seamless blend of scalability, reliability, and efficiency.
Understanding Azure Container Apps Architecture
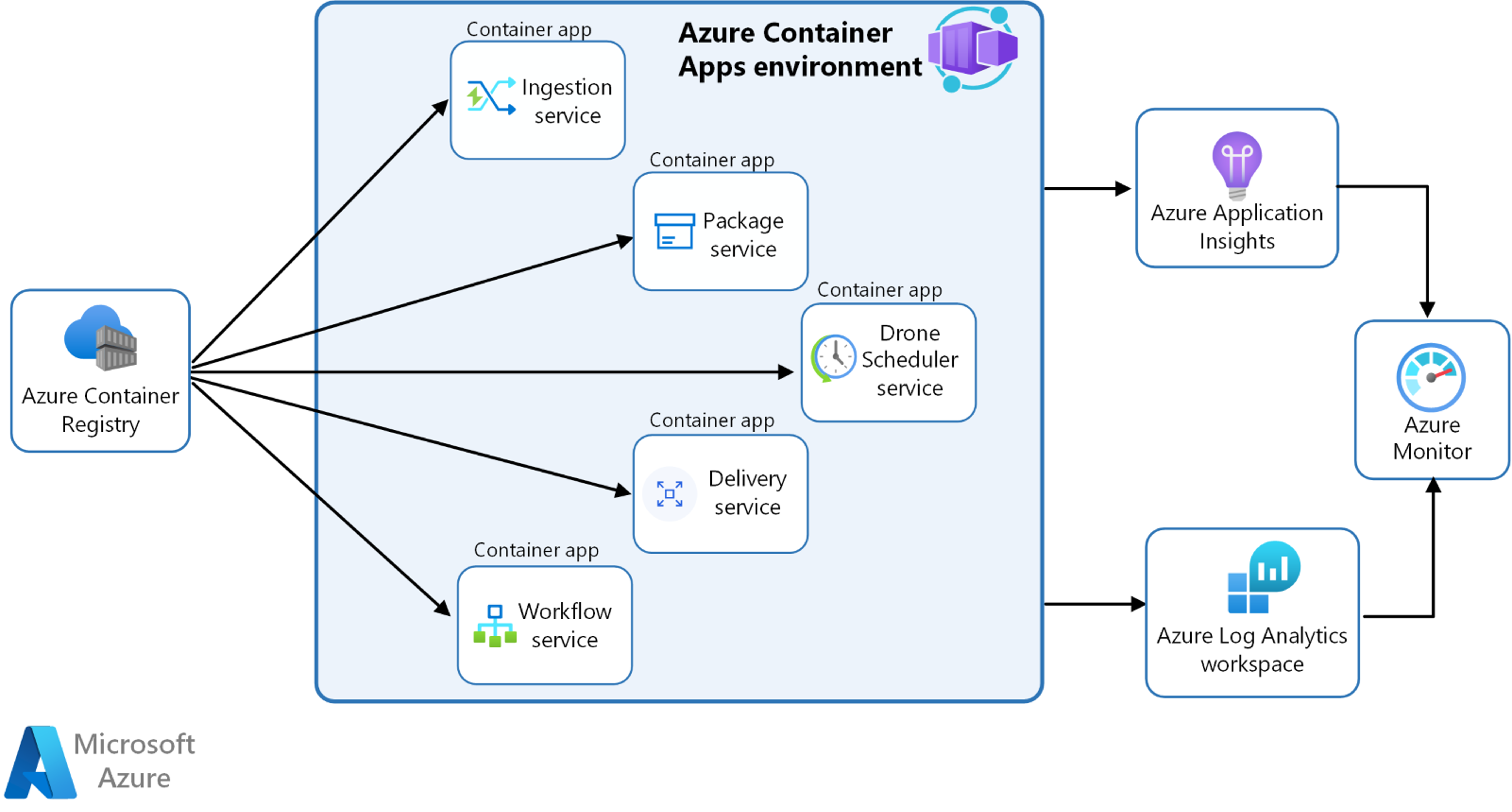
Azure Container Apps provides a fully managed serverless container platform that enables organizations to run microservices and containerized applications without managing complex infrastructure. At its core, the service builds upon Kubernetes concepts while abstracting away the operational complexity.
Source: Microsoft Learn
Environments: Secure Boundaries for Container Apps
The platform's architecture consists of several key components, one of which is the environment. An environment provides a secure boundary around a group of container apps, encapsulating networking, storage, and other shared resources. This ensures isolation and security between different application groups, allowing multiple environments to coexist within a single Azure Container Apps instance.
Revision Management: Seamless Application Updates
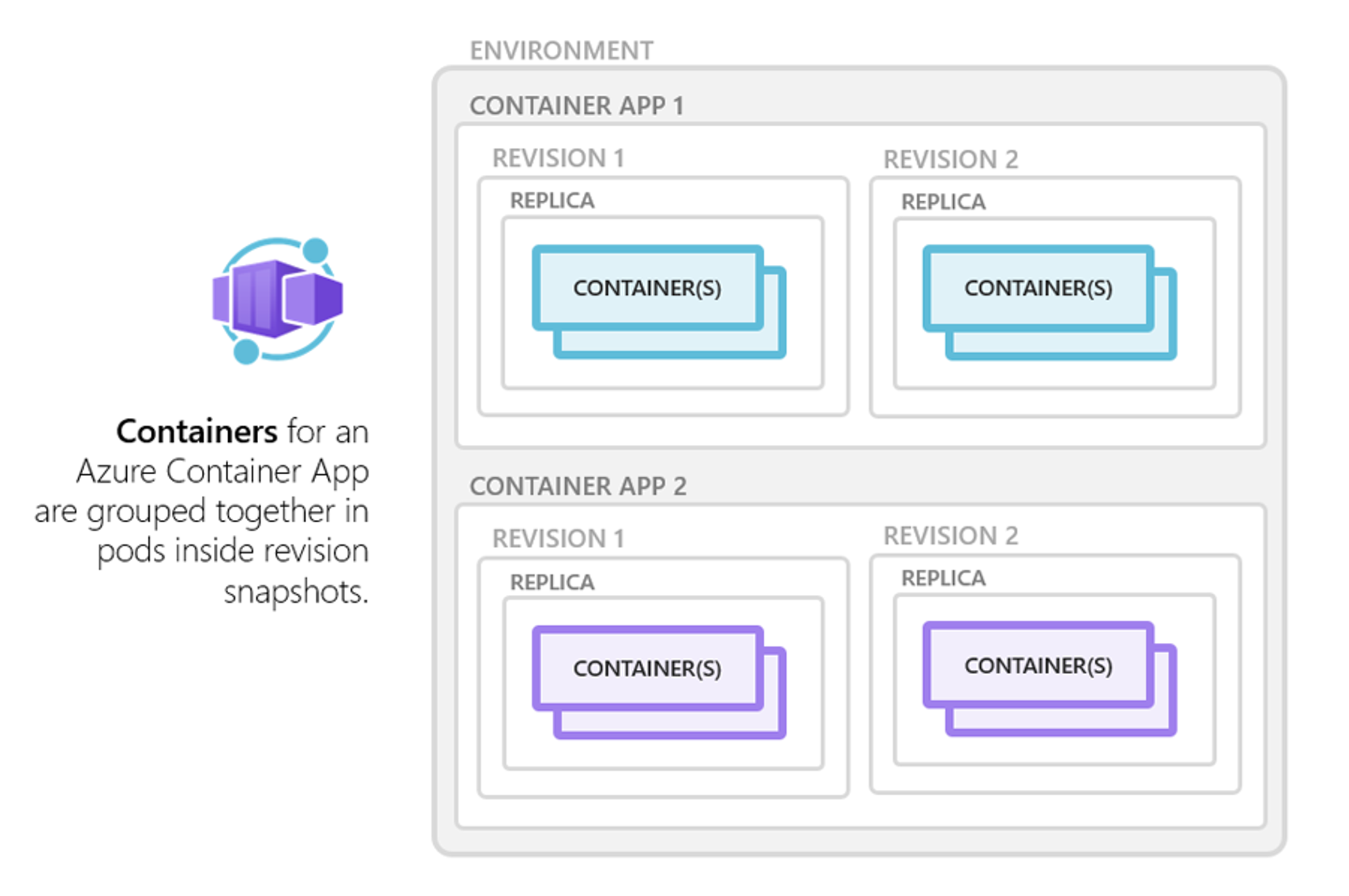
Azure Container Apps also includes built-in revision management for application updates. Each time an application's code or configuration is updated, a new revision is created. This enables easy rollbacks to previous versions if issues arise, ensuring a smooth and controlled deployment process. Revisions provide a clear history of application changes over time.
Source: Microsoft Learn
Automatic Scaling: Handling Dynamic Workloads
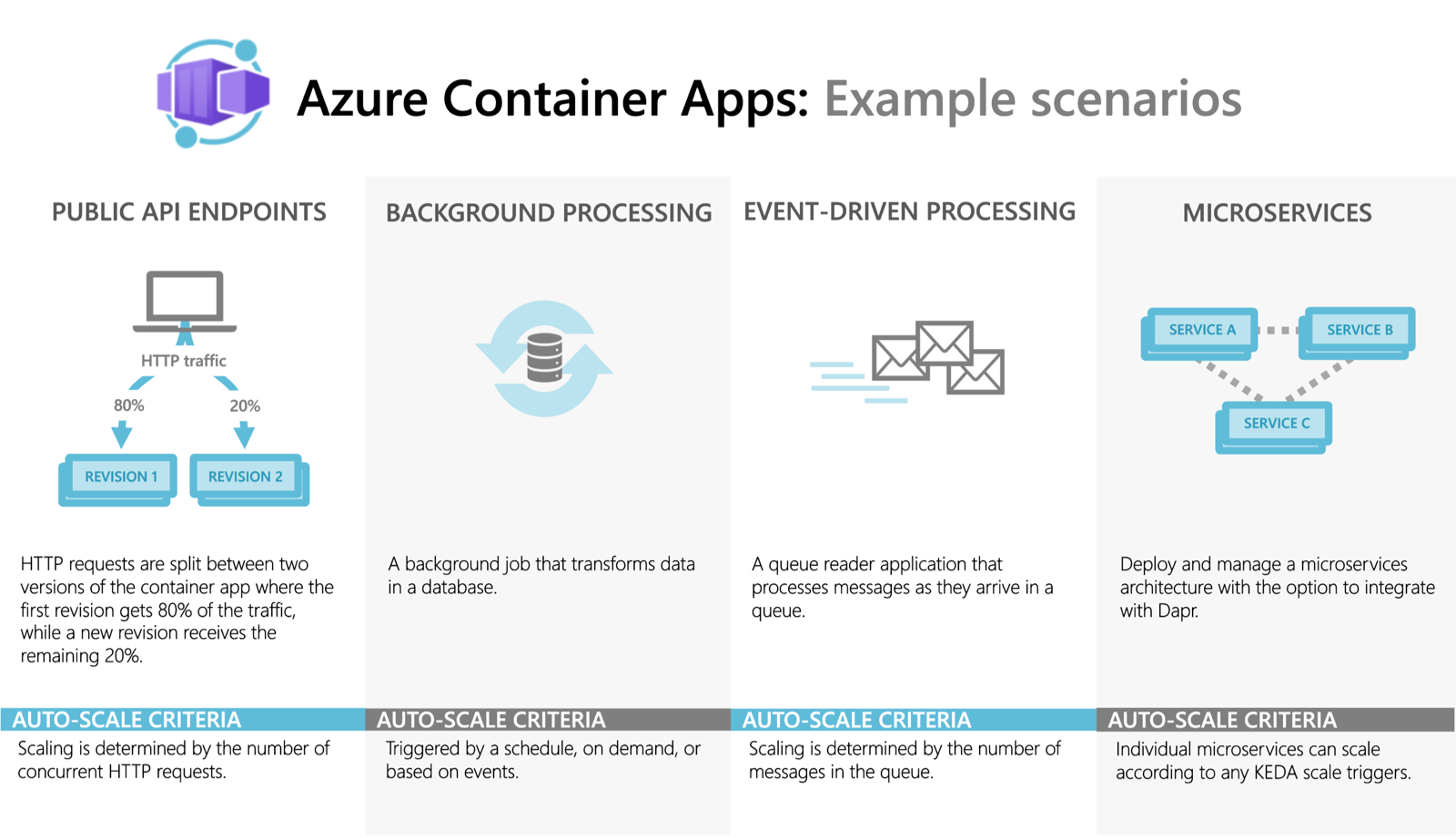
One of the key benefits of Azure Container Apps is its automatic scaling capabilities. The platform supports scaling based on various metrics, such as HTTP traffic, events, or custom metrics. Organizations can define scale rules to automatically adjust the number of container instances based on the incoming load. This ensures that applications can handle sudden spikes in traffic without manual intervention, providing a seamless user experience.
Source: Microsoft Learn
Service Discovery: Simplifying Microservices Communication
Azure Container Apps includes built-in service discovery using internal DNS resolution. Services within the same environment can communicate with each other using their service names, eliminating the need for hard-coded IP addresses or complex service discovery mechanisms. This simplifies the development and deployment of microservices architectures, as services can easily locate and interact with each other.
Docker Integration and Containerization
Docker serves as the foundation for container image creation and management within Azure Container Apps. The integration process begins with creating optimized Docker images for applications. Here's an example Dockerfile that demonstrates the containerization of a .NET application:
```dockerfile
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/aspnet:6.0
WORKDIR /app
COPY bin/Release/net6.0/publish .
ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "YourApp.dll"]
```
This Dockerfile uses the official Microsoft .NET 6.0 ASP.NET Core runtime image as the base, sets the working directory to /app, copies the published application files to the container, and specifies the entry point command to run the application.
You may also like: Your Guide to Azure Marketplace
Flexible Container Registry Options
Azure Container Apps supports both public and private container registries, enabling organizations to maintain full control over their container images. Integration with Azure Container Registry provides enterprise-grade security features, such as role-based access control (RBAC), and enables seamless deployment workflows. Organizations can choose the registry option that best suits their security and compliance requirements.
Real-World Example: Migrating a Monolithic Application
Consider a scenario where an enterprise has a monolithic application running on virtual machines. To improve scalability and maintainability, they decide to migrate to a microservices architecture using Azure Container Apps and Docker.
The migration process can be a big undertaking for technical teams. It involves breaking down the monolithic application into smaller, independently deployable microservices. Alongside the migration effort, each microservice is containerized using Docker, with its own Dockerfile specifying the required dependencies and runtime environment.
The development team creates a CI/CD pipeline using Azure DevOps to automate the build, test, and deployment process. Whenever changes are pushed to the source code repository, the pipeline triggers a build, creates Docker images, and deploys the updated microservices to Azure Container Apps.
With Azure Container Apps' automatic scaling and service discovery features, the microservices can seamlessly communicate with each other and handle varying workloads. The platform automatically adjusts the number of container instances based on the defined scale rules, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Monitoring and Observability
To ensure the health and performance of the microservices, the enterprise leverages Azure Monitor and Application Insights. They collect logs, metrics, and traces from the container apps and visualize them in real-time dashboards. This provides valuable insights into the application's behavior, allowing the team to quickly identify and troubleshoot any issues.
By instrumenting the microservices with distributed tracing, the team gains end-to-end visibility into the request flow across different services. They can identify performance bottlenecks, optimize resource utilization, and ensure a smooth user experience.
Conclusion
Azure Container Apps, combined with Docker containerization, provides a powerful platform for modern enterprise application deployment. By leveraging serverless container architecture, automatic scaling, and seamless CI/CD integration, organizations can build scalable, reliable, and cost-effective solutions.
The example of migrating a monolithic application to a microservices architecture demonstrates the benefits of this approach. With Azure Container Apps and Docker, enterprises can accelerate their digital transformation journey, improve agility, and deliver innovative solutions to their customers.
As the enterprise landscape continues to evolve, embracing containerization and serverless technologies becomes increasingly crucial. Azure Container Apps and Docker provide the tools and capabilities necessary to modernize application deployment and stay ahead in today's competitive market.
Contact us today to discover how our services can help your business succeed. Our expert team provides tailored solutions to optimize your technology infrastructure, enhance productivity, and drive growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I deploy a Docker container to Azure?
Yes, you can deploy Docker containers to Azure using Azure Container Apps, which offers a seamless and fully managed way to run containerized workloads in the cloud. With this service, you don’t need to manage underlying infrastructure like virtual machines or orchestrators. Instead, you get a platform that handles scaling, load balancing, and lifecycle management automatically. Whether you’re deploying a single container or a complex microservices architecture, Azure Container Apps simplifies the process while offering flexibility, integration with CI/CD workflows, and support for modern DevOps practices. This makes it an ideal choice for developers looking to quickly move from local development to scalable, cloud-native deployments.
How to deploy a container in Docker?
To deploy a container in Docker, you start by writing a Dockerfile, which defines the application's base image, working directory, dependencies, and startup command. For example, to containerize a .NET 6.0 app, you might use the official Microsoft ASP.NET image as the base. After writing the Dockerfile, use docker build to create an image and docker run to deploy the container locally. This image can then be pushed to a registry and deployed to platforms like Azure Container Apps.
How to deploy a microservice in Azure?
Deploying a microservice in Azure is straightforward with Azure Container Apps, which is purpose-built for running containerized microservices. First, package each microservice as a Docker container. Then, push the images to a container registry, such as Azure Container Registry or Docker Hub. After that, you can create Container Apps for each microservice, either individually or as part of an environment that supports features like:
- Automatic scaling based on HTTP traffic, event streams, or custom metrics
- Dapr integration for service discovery, pub/sub messaging, and observability
- Built-in ingress for secure, public access to your services
- Secrets management and environment variables for configuration
This approach allows your microservices to operate independently, scale individually, and communicate reliably—without needing to set up or manage complex Kubernetes infrastructure. It's a powerful way to build modern, distributed systems in Azure.
What is the purpose of Azure Container Apps?
The primary purpose of Azure Container Apps is to provide a serverless container platform that enables developers to run microservices and other container-based applications without having to manage underlying infrastructure or orchestrators. It offers a balance between simplicity and control, combining the flexibility of containers with the ease of a fully managed platform.
Key capabilities include:
- Automatic scaling based on HTTP traffic, event-driven processing, or custom KEDA (Kubernetes Event-Driven Autoscaling) rules
- Built-in ingress and traffic splitting for blue-green or canary deployments
- Dapr integration for building resilient, event-driven, and service-to-service communication patterns
- Support for multiple revisions, so you can deploy updates without downtime
Azure Container Apps is ideal for scenarios where you need rapid deployment, efficient scaling, and simplified DevOps workflows, especially in distributed or microservice-oriented applications. It brings the best of containers and serverless computing together in one cohesive environment.





