Artificial intelligence (AI) has been making headlines recently. Whether you’re making questionable crochet narwhals or generating hip-hop lyrics about meat, it’s clear that the latest generation of AI tools can provide a lot of entertainment.
But is AI valuable to your business? What AI tools exist these days and should you be adopting them yet?
Keep reading to learn more about what artificial intelligence is and whether you should be using it in your organization.
What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence, or AI, is when software is programmed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. Examples of these tasks include detecting patterns in data, analyzing complex financial models, and developing new products. AI is capable of performing such a wide range of tasks because it can learn and adapt to new information over time. This means that as it gathers more data, it becomes better at performing its assigned tasks.
AI is designed to imitate human behaviors and capabilities—in fact, it even wrote the paragraph above (this wouldn’t be a proper Intro to AI without that bit 😏).
Long before artificial intelligence was tweaking our social media feeds and serving up Google search results, books and films familiarized us with the idea of “intelligent” anthropomorphic machines that could think like humans. That probably contributes to some misconceptions (and unease) around AI. So let’s move away from vague terms and talk about some of the specific capabilities modern artificial intelligence has.
Machine learning
Machine learning is the way we train machines to recognize patterns in data and draw conclusions from those patterns. It often lays the foundation for an AI system.
Anomaly detection
Anomaly detection is the ability to automatically detect errors or data points that deviate significantly from the rest of the data. For example, it’s used to detect things like fraudulent credit card activity or tumors on an MRI image.
Computer vision
Computer vision allows software to recognize and interpret images and videos. For example, computer vision is key to self-driving vehicles, which use it to understand things like traffic lights, signs, and other vehicles on the road.
Natural language processing
Natural language processing gives computers the ability to interpret written or spoken language and respond in kind. You’ve probably already interacted with natural language processing systems a lot, like when you use predictive text on your phone or get a search result that matches your intent but not your exact wording.
Knowledge mining
Knowledge mining involves extracting information from large, often unstructured sets of data. It can index the data for easy searches and provide insights.
What is generative AI?
Artificial intelligence is nothing new, so why have we been hearing about it so much lately?
Most of the news is about recent breakthroughs in generative AI. Generative AI is artificial intelligence that can learn from input to produce new content. For example, if it’s trained on examples of code, it can turn around and create its own unique code that’s (in theory, at least!) semantically and syntactically correct.
OpenAI has released a new set of generative AI apps that have taken the world by storm. ChatGPT can generate text that’s almost indistinguishable from human writing, whereas Dall-E takes text input and creates images (which are impressive, but a bit weirder if we’re honest).
Let’s take a look at how generative AI fits into the artificial intelligence landscape.
At the highest level, we have artificial intelligence, or software that imitates human behavior. Machine learning, as we’ve already discussed, is a subset of AI. Machine learning models take in data and fit the data to an algorithm in order to make predictions.
Next we have deep learning, which is a type of machine learning based on artificial neural networks. These neural networks make sense of observational data by passing it through interconnected layers of nodes, generating a more complex understanding with each one. Deep learning is particularly effective for tasks such as image recognition and natural language processing.
Finally, generative AI is a subset of deep learning. While some types of deep learning focus on classifying items or making predictions, generative AI is about creating brand new content.

(Source: Microsoft AI Course)
How important is AI in 2023?
The latest advances in artificial intelligence have many people wondering: should adopting AI be a priority for your business? Or is it all just hype?
AI is worth your time
Artificial intelligence is a rapidly improving technology with a vast spectrum of potential applications. In other words, you can expect it to eventually impact your work in significant ways. Here are a few examples.
A new kind of search
In the words of Microsoft CEO Satya Nadellav, “AI will fundamentally change every software category, starting with the largest category of all – search.”
Search engines have used AI for a while, but we’re about to see artificial intelligence take on a much bigger role. Think about the implications of a search engine that can understand the intent of almost any query in a nuanced and conversational way—and generate on-demand answers using the entire internet and all publicly available data as its knowledge base. From a business perspective, this will change the way we connect with our audience. Content strategy, SEO, UI/UX and more will all be affected.
Industry disruptions
In their book Power and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial Intelligence, Ajay Agrawal, Joshua Gans, and Avi Goldfarb explain that we’re in the “Between Times” of AI, or the period that comes after we’ve recognized the potential of a new technology but before its widespread adoption. As a comparison, they point out that it wasn’t until around forty years after Thomas Edison invented his lightbulb for electricity to be commonplace. But of course, we all know how electricity has fundamentally changed almost every aspect of life.
The authors suggest that AI transformation will follow a similar path, starting with point solutions (areas where AI can easily replace existing tech without systemic change, such as language translation) but eventually disrupting entire industries (such as insurance and Intralogistics Solutions).
…but use caution
We’re still in the early, early days of AI. The potential is exciting, but adopting bleeding edge technology always comes with risk. Investing too much in AI right now could take time and resources away from more predictably successful initiatives.
How to prepare for the future of AI
So if artificial intelligence will transform the world, but it’s not quite time to go all in on it yet, how should you approach the new tech?
To understand more about where we are with AI, let’s look at the Gartner Hype Cycle, a graphical representation of how new technologies progress.
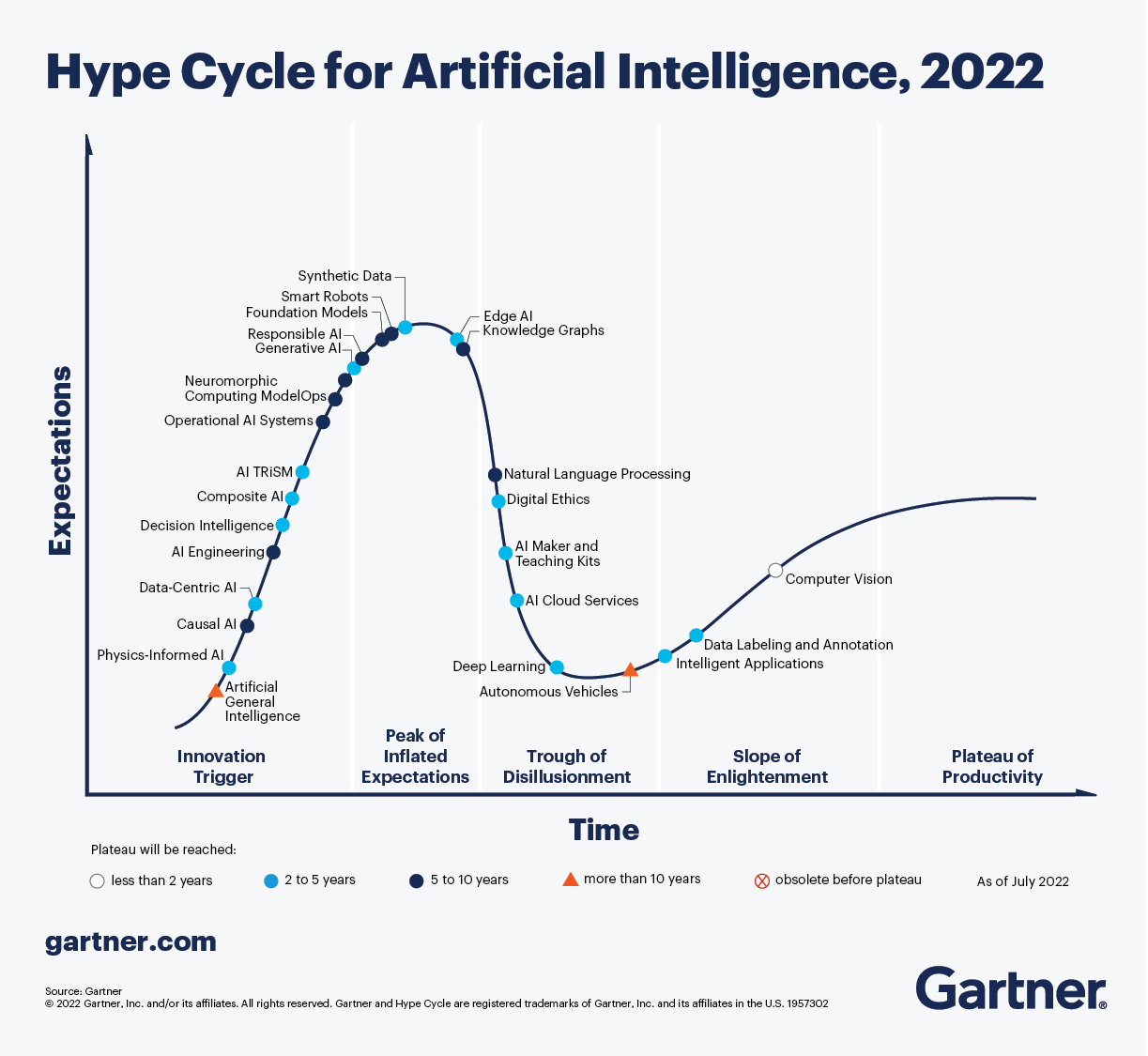
(Source: Gartner)
Right now, most aspects of artificial intelligence are on the peak of inflated expectations, the time period when early publicity gets us all excited about the potential of a technology. But after that comes the trough of disillusionment when many experiments and implementations fail. Eventually, on the slope of enlightenment, the technology becomes more widely understood and some enterprises adopt it, while others remain cautious. Finally, mainstream adoption takes off on the plateau of productivity.
Artificial intelligence is here, and companies that stay locked into the status quo will fall behind while their competitors reap the benefits on the slope of enlightenment. At the same time, investing too heavily in AI while climbing the peak of inflated expectations comes with big risks.
We recommend a gradual approach—set aside a small amount of time to learn more about AI and consider testing an AI tool for:
- Some part of your workflow (we provide some suggestions later in the article), or
- An AI service (e.g. Azure OpenAI Service) for some part of your product/application.
In addition to this “test and learn” recommendation, I recommend noting down a few principles to help you stay flexible and oriented during this phase of intense change. A principled approach to change strikes a balance between flexibility and structure. For example, the agile principles emerged as an adaptive response to the more rigid waterfall methodology that preceded them.
A few principles that I keep returning to in recent months include:
- Embrace the Conditions
- Adopt a Progression Based Mindset
- Use Risk as a Compass
These principles come from a book, Ride The Wave by John Wessinger, and have helped me navigate the past few months of AI developments because they’re general enough to apply to a variety of questions and contexts while being specific enough to help me move forward with less FUD.
How to use artificial intelligence in your business
Enough with the hypothetical—let’s look at some of the real-life ways that you can use AI today, including tools that you can use for business purposes right now.
What can AI do for you?
Writing code
One of the most intriguing uses of AI is for software development. Artificial intelligence can generate code based on massive training sets of public examples (GitHub repositories, etc). It can also help with things like bug detection, making optimization suggestions, and QA.
The new generative AI tools understand natural language, so you can use everyday speech to ask them to generate code. Initial studies and anecdotal feedback are validating the marketing message that “AI as copilot or pair programmer” is a compelling approach for how to adopt these tools.
- GitHub Copilot is an AI software development tool that our team is experimenting with and it can do things like make suggestions for your next lines of code or write code based on natural-language comments. It’s a great tool for saving time on repetitive boilerplate code.
Streamlining daily tasks
Expect AI to find its way into more and more tools designed to improve productivity and take some of the boring daily work off of your plate. For example:
- The new Bing is now publicly availabe and I’ve been enjoying chatting with it using the right-sidebar feature in the Edge browser where it can use the context of the current page to answer questions and compose additional text (for example, it helped me rephrase a few pieces of this blog post and find relevant links to include).
- Microsoft Teams Premium will feature Intelligent Recap, which enhances your Teams recordings through autogenerated chapters, suggested action items, and insights to catch up on missed meetings where your name was mentioned.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 is integrating AI in multiple places from Fraud Protection to Customer and Sales Insights.
- Microsoft Viva Sales is “a seller experience application that lets sellers use Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Teams to automatically capture data into any CRM system, eliminating manual data entry and giving more time to focus on selling.”
Content generation
As the name suggests, you can use generative AI to generate new content. For example, you can use it to write content for your website or social media posts or even to create images for ads. You shouldn’t leave AI to these tasks unsupervised, though. AI-produced content can read like it was written by a human, but it’s not always accurate. And while Google is no longer fully against AI content, it will penalize anything that it considers low-quality.
There are other ways to use artificial intelligence, like brainstorming ideas or pushing through writer’s block. For example, an AI tool like ChatGPT can quickly generate a list of potential blog post titles about a particular topic. Or you can use artificial intelligence to edit, translate, or refine content.
- ChatGPT can write natural sounding content of many different types.
- There are also tools like ai that are designed specifically around business use cases like blogging and creating ad copy.
- ai helps with research and content creation through tasks like summarizing or outlining content, continuing content that you’ve started writing, providing a counterargument to a text, generating ideas for content titles, and more.
What are the risks and challenges of using AI?
Artificial intelligence is impressive, but far from perfect. Here are a few examples of current challenges with the technology in general and how they could affect you.
Built-in bias
You might assume that artificial intelligence is impartial. It’s a machine, not a human, so how could it be biased?
Unfortunately, there have been a few well-publicized cases of AI bias. In one, an algorithm used by hospitals was more likely to assign extra care to white patients than black patients. This reflected that the AI was trained on data from past cases, which showed the same prejudice.
There are a number of ways that AI bias can affect your business. For example, imagine that you use AI to create audience segments for marketing campaigns. The artificial intelligence will look at the profiles of past buyers and create a segment of similar people. However, you might find that:
- The AI targets low-value customers over high-value customers because they’re more common.
- The AI ignores market shifts because it’s being trained on old data.
- The AI only selects people who match the majority profile. For example, a product for the tech industry will not be advertised to women and POC in tech.
Errors
AI makes mistakes. Some mistakes are extremely dangerous, like when a self-driving Tesla braked unexpectedly and caused an 8-car pileup. Using artificial intelligence in your business might not be quite so life and death, but it could be disastrous for your organization if, for example, an AI program makes a mistake with a big marketing campaign or on your financial predictions.
Data privacy problems
Artificial intelligence learns from data, and some of that data is confidential. Almost 82% of consumers are somewhat concerned or very concerned about how the use of AI for marketing, customer service, and technical support could potentially compromise their online privacy.
To maintain customer trust and ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR, businesses need to be careful about how their AI applications are collecting, storing, and using customer data.
Trust issues
Artificial intelligence has the potential to take over a lot of analysis and decision-making tasks. This is great news – AI has access to much more information than any one human and it can draw insights from that data with lightning speed.
But it can also leave us wondering where it got its information and how it made its decisions. For example, you can implement an AI-based tool that gives your sales team predictions and recommendations. But will team members trust the insights enough to follow through with them?
Liability
If a self-driving vehicle crashes or if your customer is unfairly charged for a product based on AI facial recognition, whose fault is it? And how should the liable party be held responsible for something that a piece of software did?
AI is a new and evolving technology, so there are limited precedents. Companies using AI should think about how they will respond to situations caused by AI systems.
Learn more about AI
Interested in learning more about artificial intelligence? Check out these resources:
Hands-on learning
Have fun experimenting with ChatGPT and Dall-E 2.
Online course
Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals: Get started with artificial intelligence is a course that will teach you more about topics like machine learning, natural language processing, the risks of AI, and more.
Informative and fun
- Kevin Kelly's Wired article "Picture Limitless Creativity at Your Fingertips" gives an accessible explanation of where we are in the Tech Panic Cycle.
- AI 2041is an enjoyable book that pairs short science fiction stories with expert analysis.
- Power and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial Intelligenceis a businessperson’s guide to understanding and engaging with AI. Helpful overview, but written before some recent developments so it has notable gaps.
- Wolfram|Alpha as the Way to Bring Computational Knowledge Superpowers to ChatGPT
- NYTimes Daily podcast on how new Bing is changing “The Online Search Wars”
- X-Files episode Rm9sbG93ZXJz –machines work together to get that tip 😅
Incorporate AI into Your Application
We have experience incorporating AI services into a few applications and would be happy to help you compare options and decide if now is the right time for you to do so. Please fill out our contact form and we’ll be in touch shortly.






