Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based software delivery model that allows end users to access an application without needing to manage the underlying infrastructure. Instead, the hardware and software infrastructure are managed by a third-party software provider.
This article will cover what SaaS is, how it works, and some common use cases. Read on to learn more.
What Is SaaS?
While the concept of SaaS has been around for some time, the SaaS model that we know today first emerged and gained popularity in the early 2000s. The mass adoption of the internet and advancements in cloud technology set the stage for this evolution. Tech giants were the first to offer software products over the Internet. Once it was demonstrated that the SaaS model was highly successful, it was quickly adopted across many industries.
Put simply, Software as a Service is a software distribution model that involves hosting applications with third-party providers and accessing them over the internet. The traditional software distribution model, in contrast, relies on storing applications locally on each device where the user needs to install and maintain the software to keep it working.
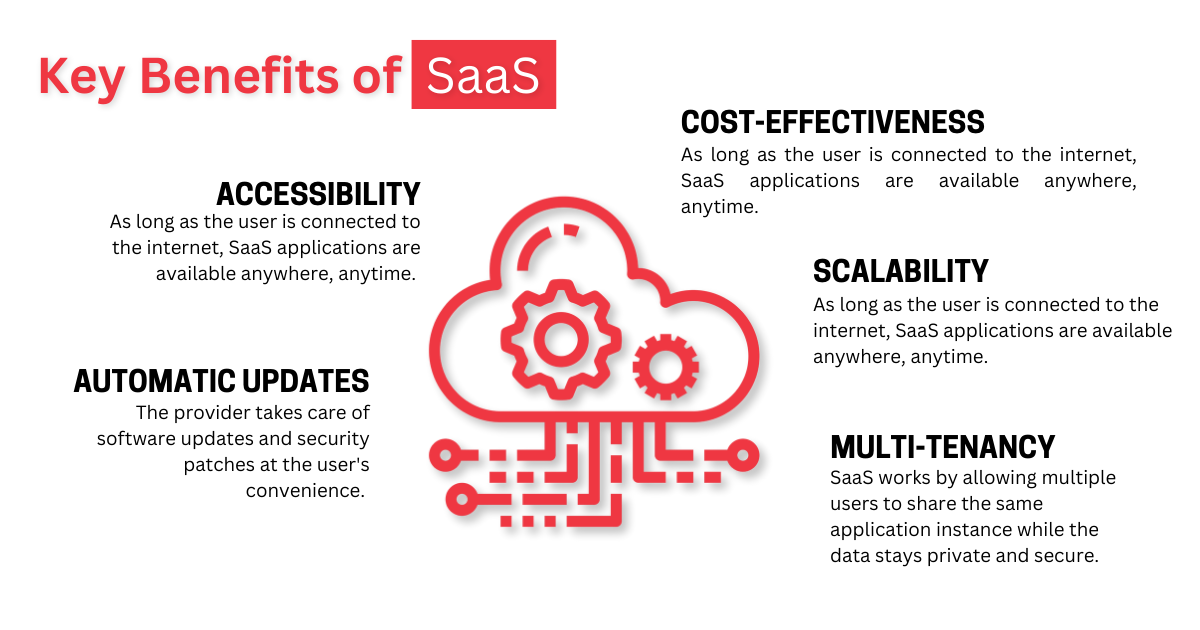
Key Benefits of SaaS
The key benefits of SaaS include accessibility, cost-effectiveness, scalability, automatic updates, and multi-tenancy.
- Accessibility - As long as the user is connected to the internet, SaaS applications are available anywhere, anytime. This is especially useful for remote work and globally distributed workforces.
- Cost-effectiveness - SaaS works on a subscription-based pricing model that spreads costs over time. There is no longer any need for upfront investments in software or hardware.
- Scalability - Since the end user doesn’t need to manage the infrastructure, applications are much easier to scale when data volumes increase.
- Automatic updates - The provider takes care of software updates and security patches at the user's convenience. Getting the latest features is effortless.
- Multi-tenancy - SaaS works by allowing multiple users to share the same application instance while the data stays private and secure. This allows for more efficient resource utilization and reduced costs.
You may also like: What Is IaaS? Infrastructure as a Service Explained
How SaaS Works
Software companies that use the SaaS delivery model can either host their applications on their own servers or via third-party providers. Their customers access these applications over the internet, usually through a web browser. This streamlines software deployment, management, and maintenance and provides a more secure but convenient user experience.
One of the most important aspects of how SaaS works is multi-tenancy architecture. Put briefly, this means that a single application instance can be provided to multiple customers (tenants) while still ensuring each customer’s data is isolated or invisible to other customers. Thanks to this architecture, SaaS providers can use resources more efficiently without compromising on security. They can also quickly release updates and features to all customers simultaneously.
Another important SaaS aspect is cloud computing. Cloud providers can supply the complete infrastructure necessary for software delivery, including servers, storage, and networking. The flexibility of such solutions allows SaaS providers to scale resources based on demand, improving performance and reducing costs. In addition to that, cloud infrastructure can significantly improve availability and redundancy.
You may also like: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS: Differences and Use Cases Explained
Common SaaS Use Cases
When it comes to SaaS use cases, the first thing that usually comes to mind is improving operations and productivity. This includes software for customer relationship management, business resource planning, and human resources.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) applications like HubSpot and Salesforce help companies manage their interactions with customers, including sales processes and marketing campaigns. They can give deep insights into customer behavior, and in turn, improve engagement and customer satisfaction.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) applications like Microsoft Dynamics and NetSuite can integrate important business processes from finance to supply chain management. By having a unified view of business operations, companies can make more informed decisions.
- Human Resource Management (HRM) applications like Gusto and Rippling are great for streamlining the entire HR process. This includes recruitment, performance and engagement tracking, and payroll. By utilizing HRM solutions, HR specialists can better manage their workforce and improve its satisfaction.
Another important use case is effective collaboration. Collaboration is a core aspect of any business and SaaS providers offer many tools to help take it to the next level. Email, messaging, and conferencing are the most common examples.
- Office application suites such as Microsoft 365 are now available as SaaS subscriptions.
- Messaging applications like Microsoft Teams can improve real-time communication with instant messaging, easy file sharing, and APIs for integrating third-party apps.
- Conferencing applications make it possible for companies and teammates to host virtual meetings, conferences, and webinars more flexibly and globally.
You may also like: Cloud Migration Techniques: What Is Lift and Shift?
Final Words
SaaS is transforming software access by providing cloud-based applications that eliminate the need for managing the underlying infrastructure. This model offers flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making complex applications accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Key SaaS features include accessibility, cost-effectiveness, multi-tenancy, scalability, and automatic updates. SaaS applications are hosted remotely and accessed via the Internet to streamline deployment and maintenance.
Common SaaS applications include CRM, ERP, HRM, and collaboration tools, with providers like Microsoft 365 leading the market.
Boost Business Efficiency with SaaS
Looking to implement SaaS solutions with your business to improve efficiency and reduce costs? Microsoft 365 might be just what you need.
We can help you make a seamless transition. So, reach out for a free consultation today.
FAQ
Here are some questions that people frequently ask about SaaS. They can provide further clarity on the topic.
What is SaaS, explained in simple terms?
SaaS is a cloud-based service where software is delivered over the Internet.
What are examples of SaaS?
Examples of SaaS include Microsoft 365 applications like Word, Outlook, and Microsoft Teams.
What is the working model of SaaS?
SaaS works by hosting software on remote servers, accessed via the Internet, and maintained by the provider.
How is SaaS delivered?
SaaS is delivered through web browsers or dedicated apps, often via subscription.
Is YouTube a SaaS?
YouTube isn’t a SaaS, it’s a video-sharing platform and streaming sce.






